
Resonance
- Movement of electrons through the p-orbital pathway is described, as conjugation, mesomeric effect and even as resonance.
- Resonance structures are a result of flow of electrons through the p-orbital pathway.
- There is a minor difference between resonance and mesomeric effect which is not considered in this article.
- There are molecules which cannot be represented by a single conventional valence structure that is a Lewis structure.
- Such molecules are represented as a combination of several Lewis structures called Resonance structures or canonical forms.
- A simple example is 1,3-Butadiene.
- The molecule can be represented with two alternate double bonds.
- Close examination of the p-orbital picture reveals that this will not sufficiently explain its structure.
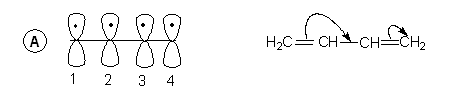
- The structure with two alternate double bonds is with the understanding, that the electrons in the p-orbitals of the carbons 1 & 2 and 3 & 4 are involved in formation of the Pi-bond as in scheme A.
- Since the four p-orbitals are adjacent to one another it is quite possible that there can be a -bond between 2 & 3 as well which leads to another structure with different distribution of electrons. As shown in B.
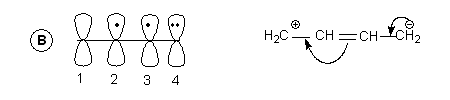
- Note: These arrangements which differ in distribution of electrons are termed resonance structures.
- It should be noted that the two structures differ only in distribution of electrons and the atoms are in the same relative positions.
- In scheme A each p orbital has one electron while in B p-orbital of C1 has no electrons hence it is positively charged . In C4 there is an extra electron hence it is negatively charged.
- Molecules can have more than two resonance structures.
- The actual molecule is considered as a hybrid of all canonical forms or resonance structures.
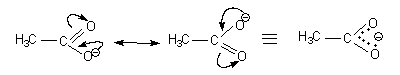
- The two structures are separated by a double headed arrow and not a reversible arrow (shown above)
- They are are not in equilibrium. They do not exist sometimes in one form and sometimes in another. They cannot be separated.
- Though resonance structures are imaginary they are very useful in explaining certain features of reaction mechanism.
Copyrights: 2005 www.chemvista.org All Rights Reserved