
1. Draw resonance structures for the following. In each case use curved arrows to show transformation and indicate the major contributor ( more stable structure)
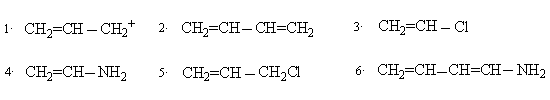
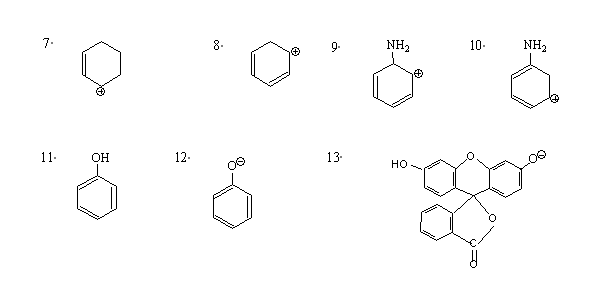
2. Differentiate resonance and tautomerism.
3. Mention two differences between resonance structures and tautomeric structures.
4. What is the bond order between carbon and oxygen in acetate anion, give an explanation.
5. The bond length between C2 and C3 is less than the normal carbon-carbon single bond. Explain?
6. In the p-orbital pictures for 1, 3-Butadiene shown below explain ?
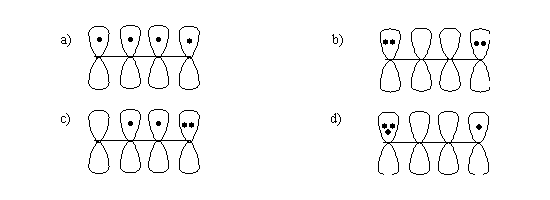
a). Which one of them is not possible?
b). Which one of them contributes most towards the hybrid?
c). Which one of them contributes least towards the hybrid?
7. Of the two dienes 1, 3-Hexadiene and 1, 5-Hexadiene which is more stable? Give an explanation.
8. Draw all the possible Lewis structures for sulphate anion; indicate the formal charge on each atom in those structures.
Which one of them represents sulphate? Can we consider all these Lewis structures as resonance structures of sulphate anion?
Use curved arrows in converting one structure to the other.9. In one of the resonance structures of acetate anion there is movement of a bonded pair of electrons between carbon and oxygen into the oxygen atom, yet oxygen gets only one unit negative charge. Explain why?
10. In the kekule structures of benzene there are three carbon-carbon single bonds and three double bonds in the ring. Hence in the three bonds should be longer than the others. Yet X-ray diffraction studies have confirmed that all the C-C bonds in the ring have the same bond length. Give an explanation. Note: The average length of a C-C single bond is 154 pm; that of a C=C double bond is 133 pm. In benzene all C-C bond lengths are found to be about 139 pm, a bond length intermediate between single and double bond.
Note: The average length of a C-C single bond is 154 pm; that of a C=C double bond is 133 pm. In benzene all C-C bond lengths are found to be about 139 pm, a bond length intermediate between single and double bond.